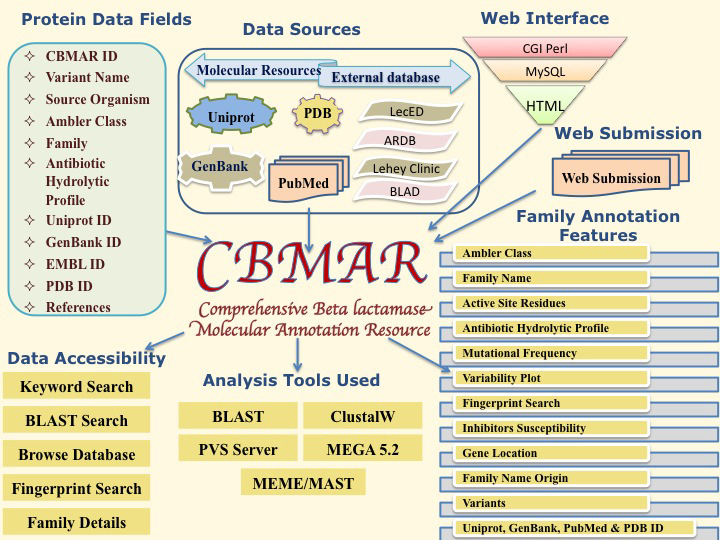
CBMAR:Comprehensive Beta-lactamase molecular annotation resource

Information & Help
| Data Content |
CBMAR provides information about molecular and biochemical functionality of β-lactamases. The basic architecture of CBMAR is based on Ambler classification. Each class is then divided into several families on the basis of their antibiotic hydrolytic profile and sequence similarity. Each family is annotated with (i) derivation of nomenclature (ii) organisms genus in which family is reported (iii) genomic location (chromosomal/plasmidic) (iv) antibiotic resistance profile (v) inhibitor susceptibility (vi) active-site (vii) family specific fingerprints (viii) mutational profile (ix) phylogenetic tree (x) names of variants. Each family is also externally linked to other sequence and structure databases. The database also supports sequence similarity searches using BLAST and search for family-specific fingerprints using MAST.
You can directly navigate to a particular section through following links:
1. Terminology Used to Describe Data Content
| Terminology Used to Describe Data Content |
| Term | Description |
| β-lactamase: | It is a super-family of enzymes using which a microbial pathogen can irreversibly hydrolyse the β-lactam class of antibiotics. |
| ID: | Each entry of CBMAR has been assigned an unique ID which can be used to locate the information pertaining to that. |
| Ambler Class: | It is the most widely used classification of β-lactamases that divides β-lactamase super-family into four classes (A, B, C and D) based upon their amino acid sequences. Class A, C and D has active-site serine while class B requires bivalent metal ion, hence popularly known as serine and metallo β-lactamases respectively. Three classes of serine β-lactamases are sufficiently different that popular alignment programs such as BLAST can't find any detectable sequence similarity, yet there is sufficient structural similarity among the three classes of serine β-lactamases that it is clear that they are homologous, i.e. descended from a common ancestor. |
| Family: | It is group of highly homologous β-lactamases which differ from each other only in few mutations. |
| Fingerprint: | It is a small strech of consecutive amino acids that are present in all members of a family. It is unique to a specific family, hence can be used to identify a family-member. |
| Active Site: | It is also small strech(s) of amino acids which play important role in the catalyis. Active site residues may not be sequentially neighbour but in the 3D space they come together to make the active site. Also all active site residues may not actively participate in the chemical reaction, they may just make the active site cavity wall. |
| Variants: | With a family, all enzymes present are not identical. They differ from each other by a few mutations, which are called as variants. |
| Gram Phenotypes: | Gram stain is the most widely used staining procedure in bacteriology. It is a differential staining procedure, which differentiates Bacteria according to their cell wall structure. Gram-positive cells have a thick peptidoglycan layer and stain blue to purple. Gram-negative cells have a thin peptidoglycan layer and stain red to pink. This field indicates the Gram-phenotype of microbes in which corresponding family of enzyme was reported. |
| Origin of Name: | It informs about the source from which family name was adopted. |
| Genera in which family is reported: | It informs all genera from which different variants of β-lactamases were reported. |
| Gene Location: | β-lactamase are present on both or either on plasmids and genome. It informs the exact location. |
| PDB ID: | It is the ID of protein structures which is experimentally determined. |
| Inhibitor Resistance: | These are chemical compound similar to the β-lactam antibiotics but have little antibiotic activity of their own. Instead they inhibit the activity of β-lactamase enzymes. |
| Hydrolytic Profile: | It lists the names of β-lactam antibiotics which is hydrolyzed by the corresponding class of enzyme. |
| Mutational Profile: | The mutational profile provides the information of all possible residues at each position in each variant of a β-lactamase family. Though it sounds similar to the variability plot, but in reality it is not. Mutational profile shows the amino acids present at a particular position whereas the variability plot only tells whether a particular position is variable or not. |
| Variability Plot: | It is generated using protein variability server. It provides variability at each position of multiply aligned protein sequences in terms of Shannon Entropy. In a variability plot higher the entropy at a position, more variable are the residues at that position while low entropy indicates a conserved region. |
| CBMAR Architecture |
| Database Schema |
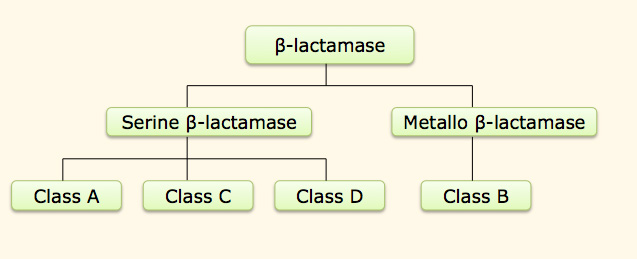
| Ambler Classification |
CBMAR Database schema is based on Ambler classification, which initially classifies β-lactamase into two classes serine based β-lactamase and zinc containing metallo-β-lactamase. The three classes A, C & D of serine β-lactamase hydrolyze their substrate by forming a serine bound acyl intermediate, whereas class B group of β-lactamase utilize active-site zinc ion to facilitate β-lactam hydrolysis and the catalysis does not requires any covalent bond formation
| Data Retreival Tools |
| Search by Keywords |
Data Input Fields:
User can perform searches using keywords, which can be source organism, PDB ID, inhibitor susceptiblity, origin of name, hydrolytic profile, gene location, gram phenotype, variants. These fields can also be chosen to display the search results. Both options are provided in the search page itself.
A keyword based search using 'carb' is shown below for example (Figure 1A).
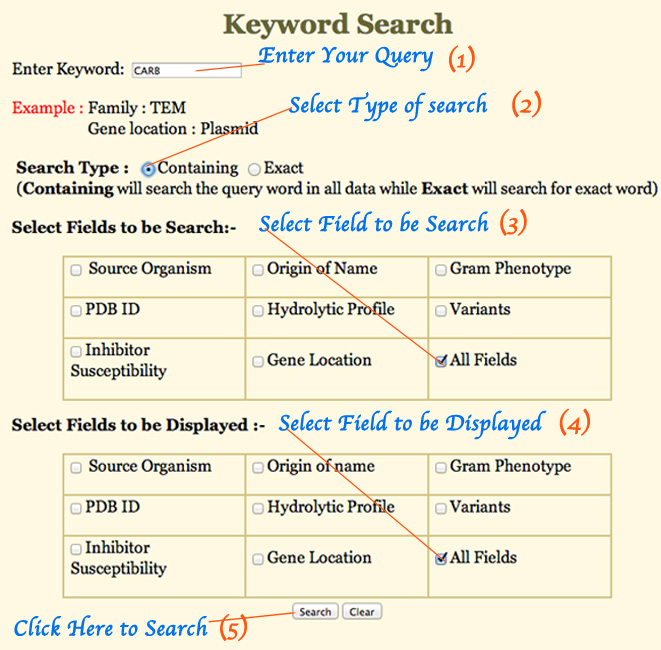
Figure 1A: - Different keyword search and display fields.
Keyword Search Result:
Extent of information in the search result depends on the fields user selected while submitting the keyword for searching. User can restrict fields to be displayed in search result. All checked fields are displayed in result. The default or if the user have not select any fields to be displayed will be CBMAR ID, Ambler class and family information. Many fields (family, fingerprint, active-site, PDB ID) in the search results are hyperlinked so that user can directly navigate to the related information.
The search result for 'carb' is shown in Figure 1B. Here both options for search and display is 'All Fields'
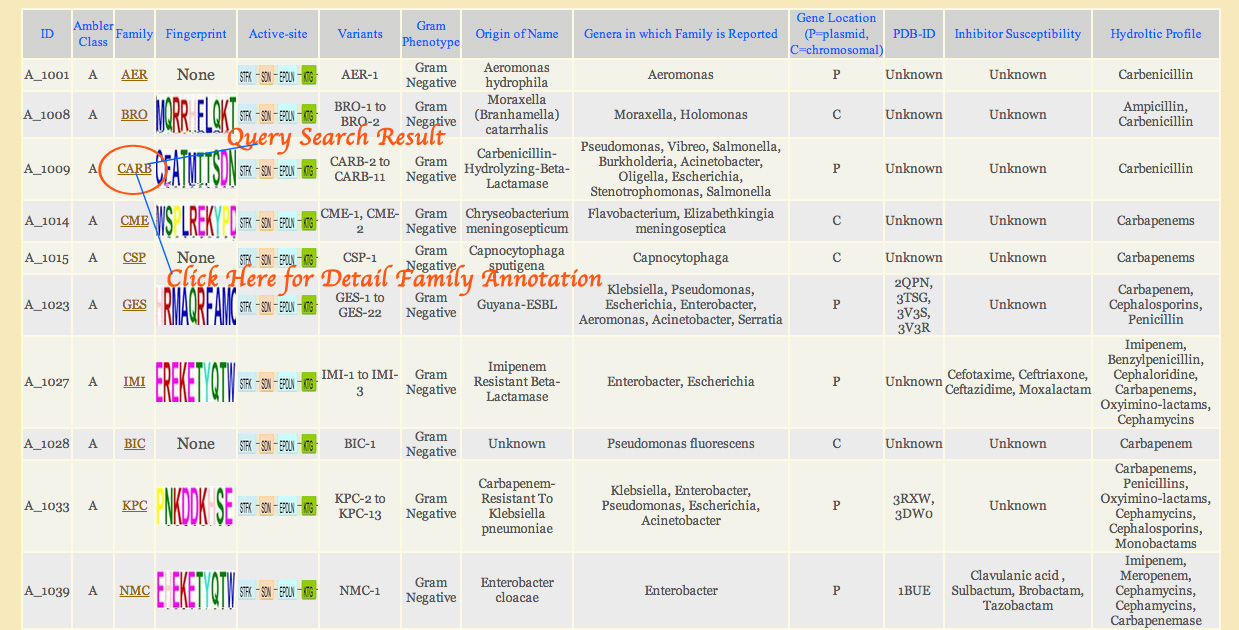
Figure 1B: - Search result for 'carb'. The option of both search and display is 'All fields'.
| Search by BLAST/Sequence |
BLAST/Sequence Search Input Fields:
User can search for the nearest homologue of their query protein/gene by searching with its FASTA format. Sequence search can be made by BLAST tool. Two different protein databases namely Uniprot and PDB β-lactamase seqeuences along with the GeneBank β-lactamase nucleotide sequences can be selected. Also the E-value can be chosen from the range of E-values provided in the drop down menu. (Figure 2A)
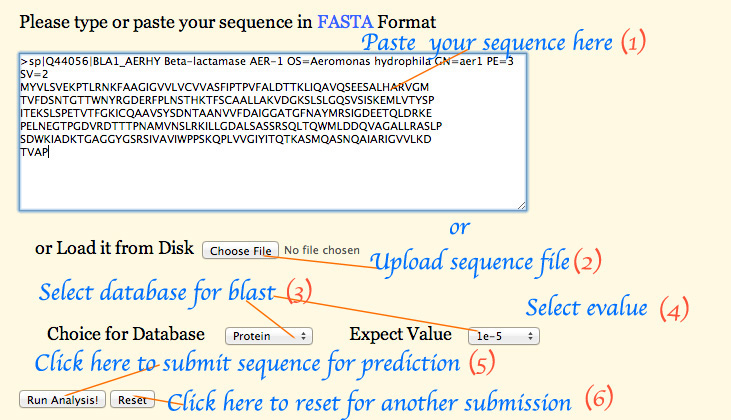
Figure 2A: - Screen shot of BLAST input page.
BLAST/Sequence Search Result:
Search result display the list of homologues in the ascending order of E-value. Each BLAST hit contains information about the AMBLER class and the family to with it belongs. (Figure 2B)
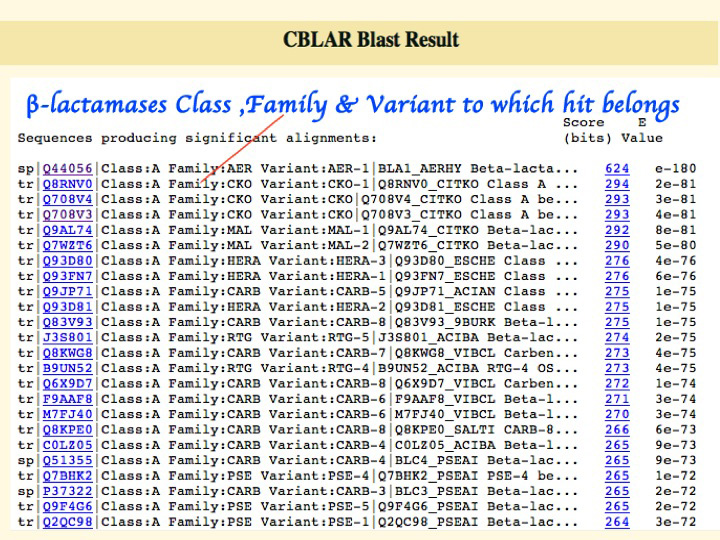
Figure 2B: - Screen-shot of BLAST search result.
| Search by Fingerprints |
It is also a sequence based search, which search for presence of a specific strech of patterns (called as fingerprint). Since each fingerprint is specific for a particular β-lactamase family, it can be used to identify the family to which the query sequence belongs. The fingerprints database is created on the basis of 605 manually curated β-lactamases protein sequences.
Fingerprint Search Input Fields:
The user have to provide the protein sequences in FASTA format to do the prediction. (Figure 3A)
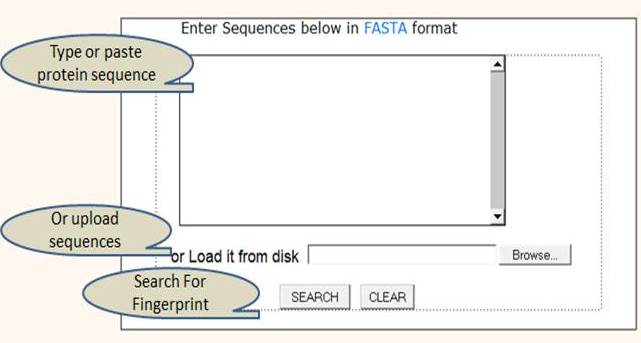
Figure 3A:- LactFp query submission page.
Fingerprint Search Result:
Output of LactFp search provides a list of top five families arranged on the basis of ascending E-value. (Figure 3B)
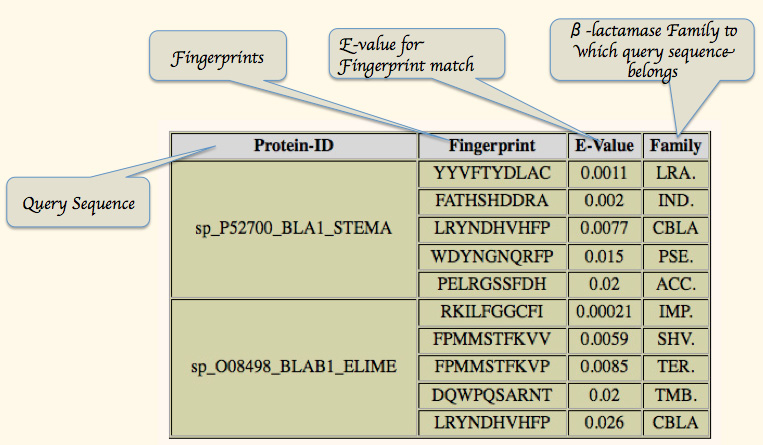
Figure 3B:- LactFp search result.
| Family Details |
It collate all information about a β-lactamase family present in the CBMAR, which includes multiple sequence alignment, variability plot, mutational profile, phylogenetic tree and Fingerprint. Families having only one sequence doesn't have multiple sequence alignment, variability plot, phylogenetic tree and mutational profile, while family having only two sequences doesn't have the phylogenetic tree (Figure 4). Family detail page can be accessed by clicking the family name in the keyword search result or from the 'Families' tab of main menu.
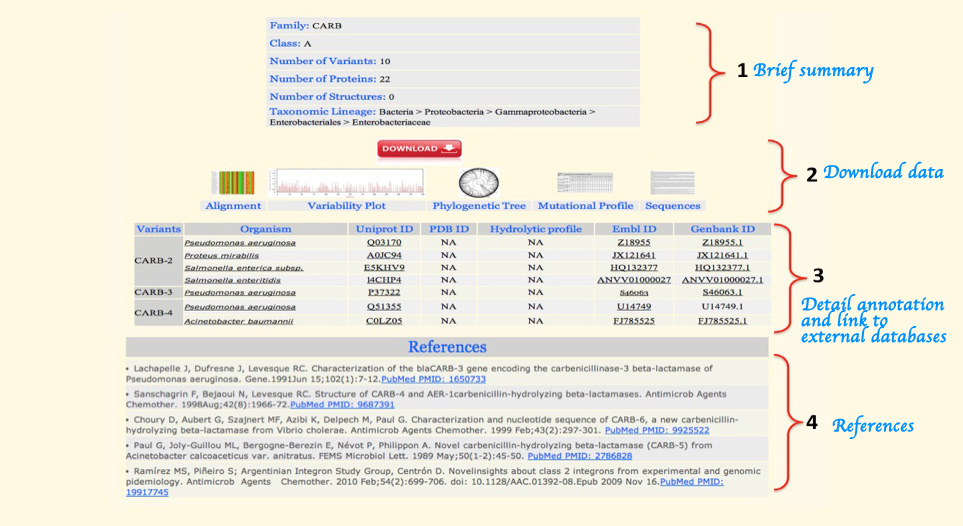
Figure 4:- Information and data present for each β-lactamase family. The sample page shown belongs to the family CARB.
1. Brief Summary of the Family:
It provides the information about data content of the family like Ambler class, sub-class (in case of class B β-lactamase), number of variants, proteins, PDB structures, and taxomic lineage (upto the common point).
2. Download:
This section includes the output of different analysis like multiple sequence alignment, variability plot, phylogenetic tree, mutation profile and protein sequences in fasta format. User can download them for further analysis.
3. Molecular Annotation and Data:
This section provides the sequence and other molecular detail of each family variant. It includes the source organism details, hydrolytic profile and links to different protein, nucleotide and structure databases.
4. References:
Reference section includes the list of research papers used for data complilation of each family.